Evolve a diversified investment strategy to stay financially sound
The goal of asset allocation is to build a diversified portfolio that balances probable returns with risk
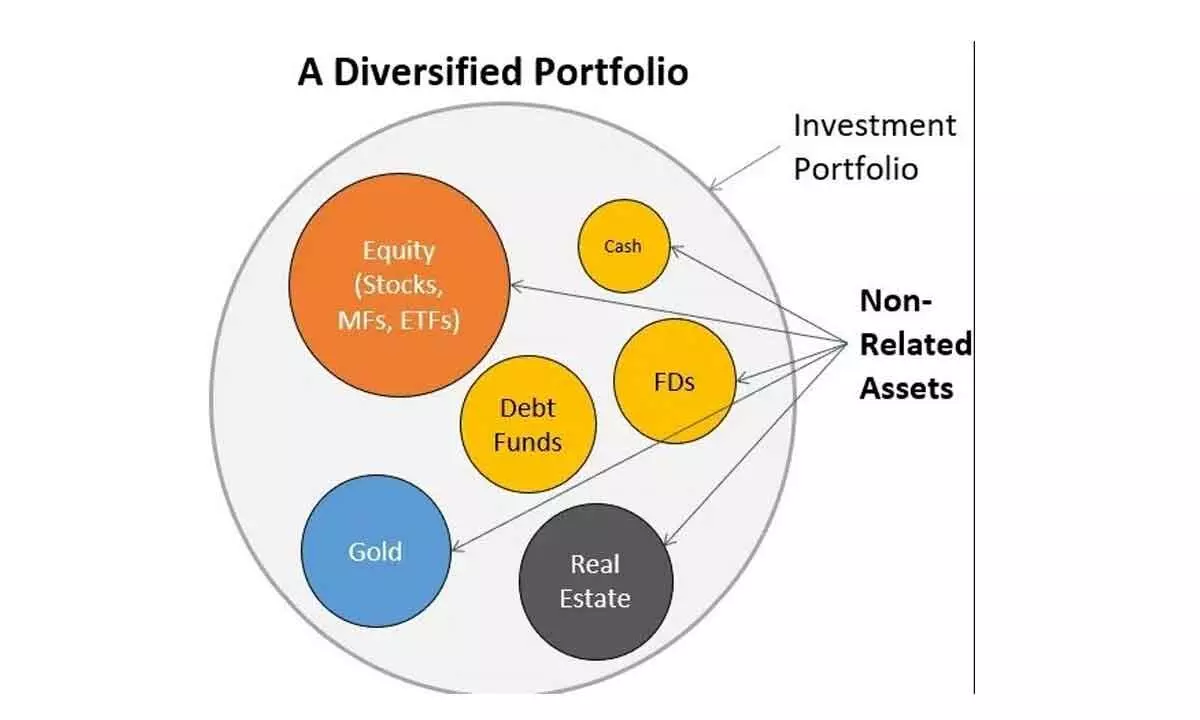
image for illustrative purpose
“Nivesh Ko Kendrit mat Karo, Soch Samajh Ki Hai Ye Baat; Vividh Asti Nivesh Ki Ran-Neeti, Deta Sankat Me Saath”
Translation: Don’t put all your eggs in one basket, it is all about planning and smart thinking; A well-diversified investment strategy is a good idea when crisis is looming.
Investing is like playing Test cricket in which you need discipline, determination, patience and perseverance to become better. Long-term investment requires these attributes, irrespective of whether you want to invest for a child’s better future, retirement corpus or wish to beat inflation.
Asset allocation is an investment strategy that involves spreading your investment portfolio across asset classes, such as equity, bonds, cash, real estate or commodities and alternative investment, whereas diversification is the spreading of your investments both among and within different asset. The goal of asset allocation is to construct a diversified portfolio that balances probable returns with risk. Asset allocation aims to achieve financial objectives while managing exposure to market instability. Asset allocation helps in spreading your investments across different asset classes to reduce the impact of inferior performance in any single investment on your overall portfolio. Diversification can augment stability and possibly increase returns over the long term.
Risk tolerance and time horizon are critical factors in determining your asset allocation. Younger investors with a longer time horizon might have a higher tolerance for risk, while those approaching to retirement might opt for a more conservative allocation.
Developing a portfolio with a low correlation between asset classes will help investors in reducing risk through diversification and may offer benefits of optimal returns over time.
Asset correlation is a measure of how asset classes move in relation to one another over a period. The correlation coefficient, a statistical measure of the correlation between two variables can range from -1 to +1. When assets move in the same direction at the same time, they are considered to be positively correlated. When one asset tends to move up when the other goes down, the two assets are negatively correlated. Zero Correlation means that two asset classes are unrelated to each other.
There are various principles of asset allocation like diversification, risk tolerance, time horizon, investment goals and market conditions.
Diversification: In asset allocation, the theory of ‘one size fits all’ does not apply. Asset allocation is done based on various factors such as age, income flow, the need for investment whereas Diversification is a way of asset allocation. The diversification strategy helps to allocate funds in different investment areas to reduce risk and increase the reward.
Risk profile: Figuring out your risk tolerance isn’t easy, and it can change over time — just like other aspects of your life. To understand risk profile, one need to understand three components that constitute risk profile – risk appetite, risk capacity, and risk tolerance. Risk appetite is how much risk you are willing to take; risk capacity is how much risk you can take and risk tolerance is how much risk you can tolerate mentally. Of the three risk parameters, risk tolerance is most critical while determining your asset allocation.
Time horizon: Time horizons help you decide the type of investment vehicle to consider, which investments to avoid, and how long to hold your investment. Volatility is often a greater risk short term than in the long term.
Investment goals: Your financial goals, such as retirement, education funding, or wealth preservation, will influence the asset allocation strategy you choose. Different goals may require different levels of risk exposure. Market conditions: Market situations and economic cycles can influence the performance of different asset classes. Adjusting your allocation based on market outlook can help to manage the risk.
Common asset classes-Equities: Stocks represent ownership in a company. They have the potential for high returns and also come with higher volatility. They are suitable for long-term growth-oriented investors.
Bonds (Fixed income): Bonds are debt securities issued by governments or corporations. They offer regular interest payments and are generally considered lower risk compared to equity.
Gold: Having gold in your investment portfolio is beneficial because it lowers risk through diversification.
Other options that can duly considered:
Real Estate/REITs, commodities andalternative investments like hedge funds, private equity, venture capital and other non-traditional investments.
Creating an asset allocation strategy:
Step 1: Assess your financial goals, risk tolerance, and time horizon.
Step 2: Select asset classes that align with your goals and risk profile.
Step 3: Determine the percentage of your portfolio allocated to each asset class.
Step 4: Regularly review and rebalance your portfolio to maintain the desired allocation as market conditions change.
Every individual’s financial condition is different and requires a unique and different approach. In fact, investors should regularly check their financial strategies and ensure that they align with their financial goals, risk profile and investment horizon.
(The writer is senior Vice-president, SBI Funds Management Ltd; Translation and text by Dr. Ajay Mittal, Sr. Vice-president and Head (Knowledge- Management) SBI Funds Management Limited)

